Strategically Using CPP To Reduce Risk In Retirement
The majority of people choose to start CPP as early as possible. In fact, over 9 out of 10 people choose to start CPP at or before the age of 65. This means that the majority of people aren’t using CPP strategically to reduce risk in retirement.
The way CPP works means that it can be a great tool to help absorb inflation rate risk and investment risk in retirement. But many people choose to ignore these benefits (or aren’t aware of them in the first place) and simply start CPP as soon as possible.
One common strategy we’ll review in this post (but not the only strategy) is to delay CPP to age 70. By delaying CPP by 10-years the payments are over 200% higher than at age 60. There is a 0.6% increase for each month of delay between age 60 and age 65. Plus, there is a 0.7% increase for each month of delay between age 65 and age 70.
Delaying CPP to age 70 is a great way to reduce risk in retirement but it’s not necessarily the best decision in all situations. There are a few other CPP strategies we can use to help reduce risk in retirement if faced with certain circumstances. This could include low investment returns, negative investment returns, or high inflation.
Rather than start CPP at age 60, or delay CPP to age 70, we can choose to start CPP at different times depending on the circumstances. This flexibility can help us decrease risk in retirement and provide more flexibility.
There are four CPP strategies we can use to help decrease risk in retirement. The first, delaying CPP to age 70, is relatively well known, but the other three strategies we’ll cover in this post are unique and can be used if faced with certain circumstances between age 60 and age 70. This provides a retiree with some flexibility to optimize their CPP start date depending on the circumstances at the time.
Strategy #1: Delay CPP To Age 70
The first and best strategy to reduce risk in retirement is of course to delay CPP to age 70. Every year of delay adds 7.2% to 8.4% to CPP payments. Delaying CPP transfers investment and inflation rate risk to the government.
Investment and inflation rate risk are reduced because investment assets are drawn down as CPP is delayed between age 60 and age 70. This decreases risky investment assets and increases an inflation adjusted pension that lasts a lifetime.
By delaying CPP it reduces two types of risk, it reduces investment risk because investment assets are drawn down to create retirement income as CPP is delayed, and it reduces inflation rate risk because delaying CPP creates a larger CPP payment that is inflation adjusted for the rest of retirement. Both investment risk and inflation risk are hard to manage for the individual investor, so decreasing this risk in a simple & flexible way is very, very attractive.
However, delaying CPP isn’t great for everyone. Delaying CPP is perfect for those who expect a long and healthy retirement, but it’s not great for those who might have a shorter than average life expectancy. It’s also not great for those who don’t have enough investment assets to draw down while delaying CPP between age 60 and age 70. Lastly, it’s terrible for low-income retirees whose GIS payments are reduced by 50%-75% of each extra dollar of CPP.
But for the typical retiree, delaying CPP to age 70 can help improve the success rate of a retirement plan by providing a larger inflation adjusted lifetime pension.
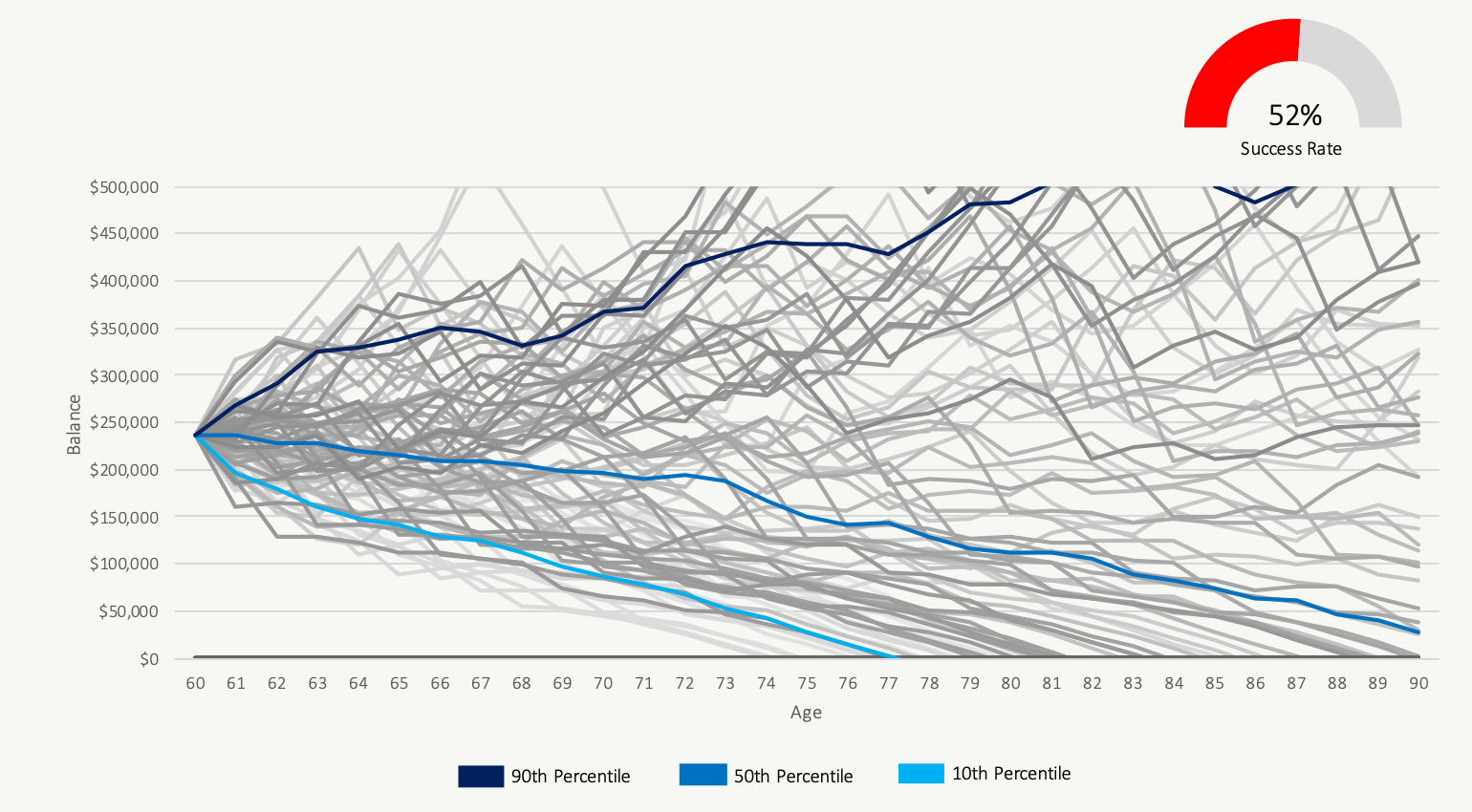
Taking CPP At Age 60
$250,000 Investment Assets And $6,400/yr in CPP
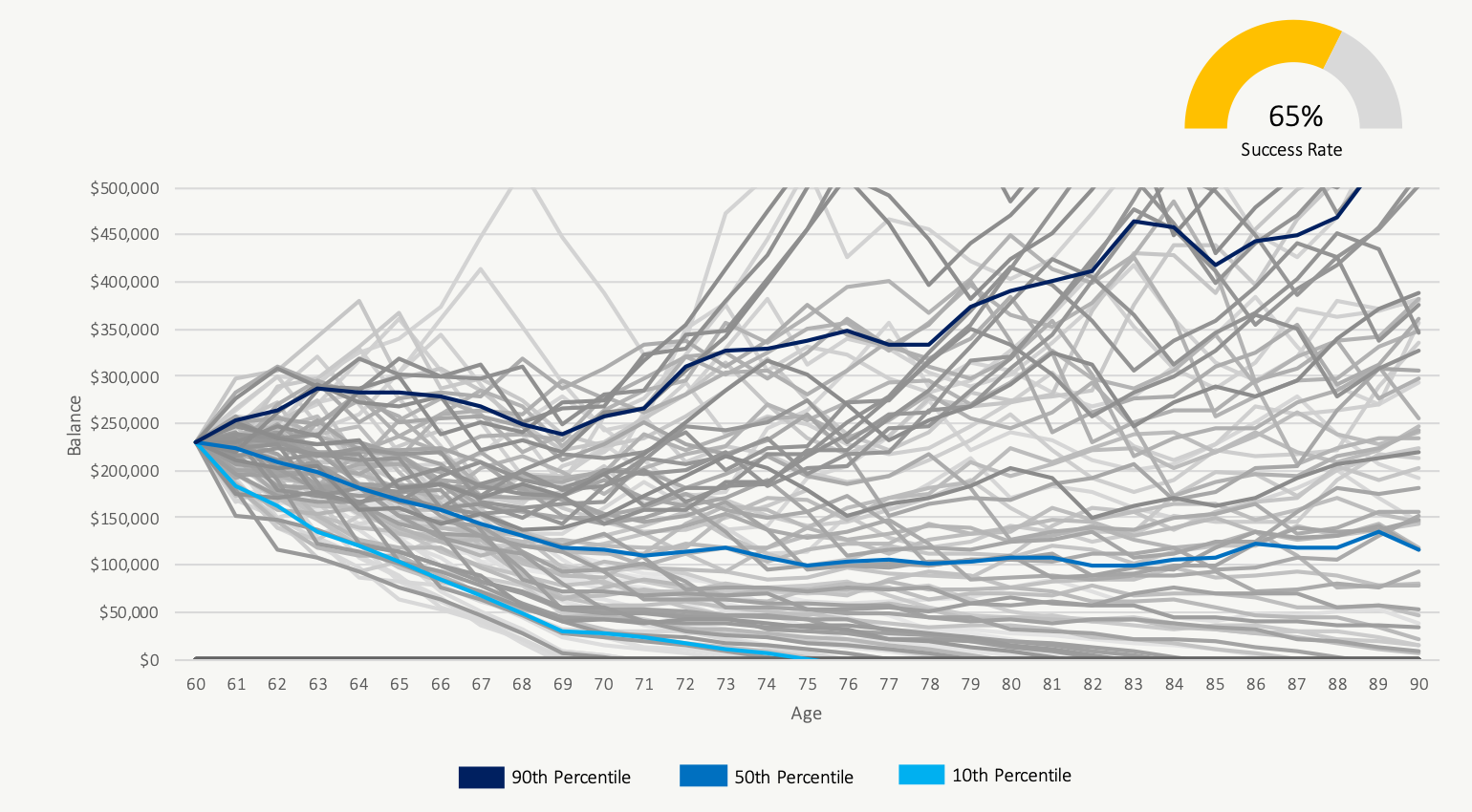
Taking CPP At Age 70
$250,000 Investment Assets And $14,200/yr in CPP
Strategy #2: Plan To Start CPP Earlier If Faced With Poor Investment Returns
Delaying CPP to age 70 is great… until investment returns turn negative. One of the big benefits of CPP is that payments can begin at any time between age 60 and age 70. This is a strategic advantage because although the default strategy can be to delay CPP to age 70, these benefits can actually begin at any time depending on the circumstances. This can be an advantage if a retiree faces a series of poor investment returns early in retirement.
If faced with a series of poor investment returns between age 60 and age 70 a retiree may choose to start CPP earlier than age 70 to help reduce the draw on their investment assets if their portfolio has temporarily decreased in value.
This can be a great advantage if faced with a correction, recession, or depression in early retirement.
Using the example from above, we see that a certain number of historical periods end in failure when CPP is delayed to age 70. This is because of a poor sequence of investment returns between age 60 and age 70 in combination with heavy withdrawals from the investment portfolio.
If we isolate these scenarios as in the charts below, we can see that taking CPP at age 60 is better when faced with a series of poor investment returns early in retirement. In these situations, investment assets will last longer if CPP is started earlier.
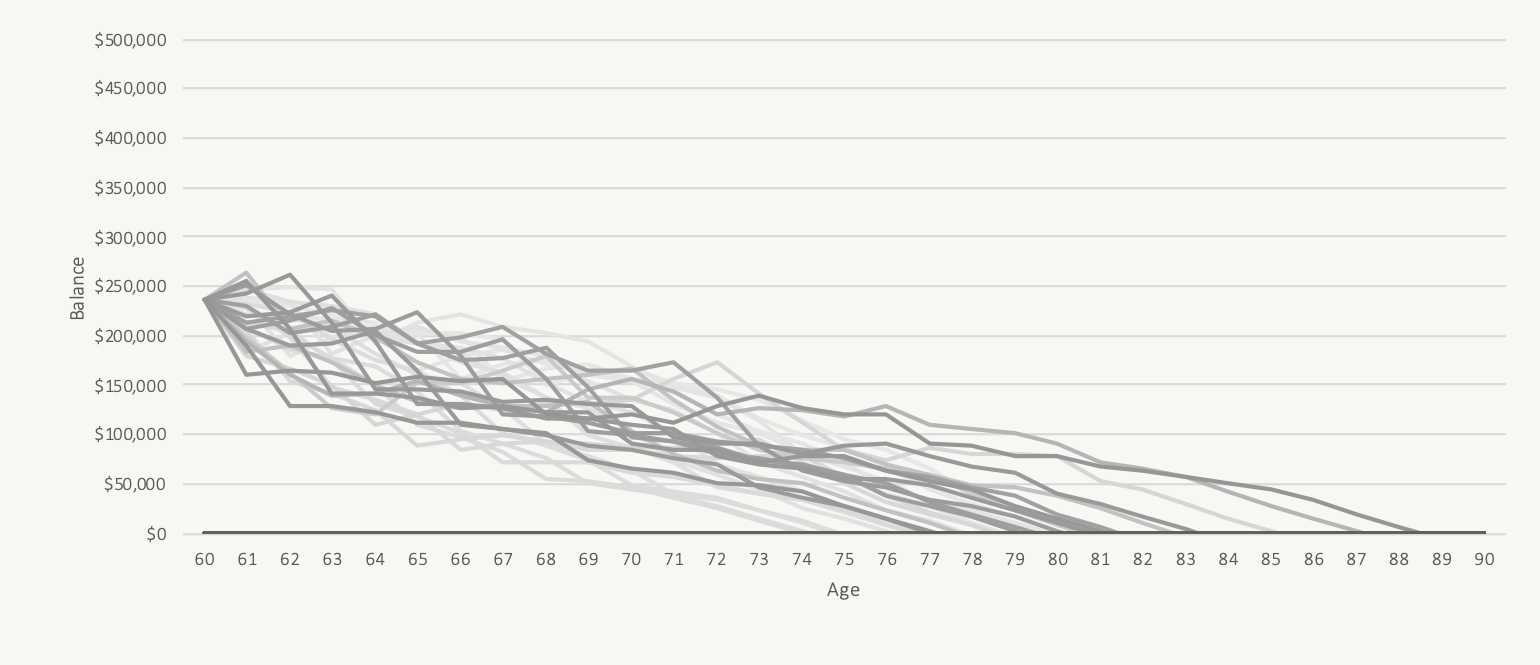
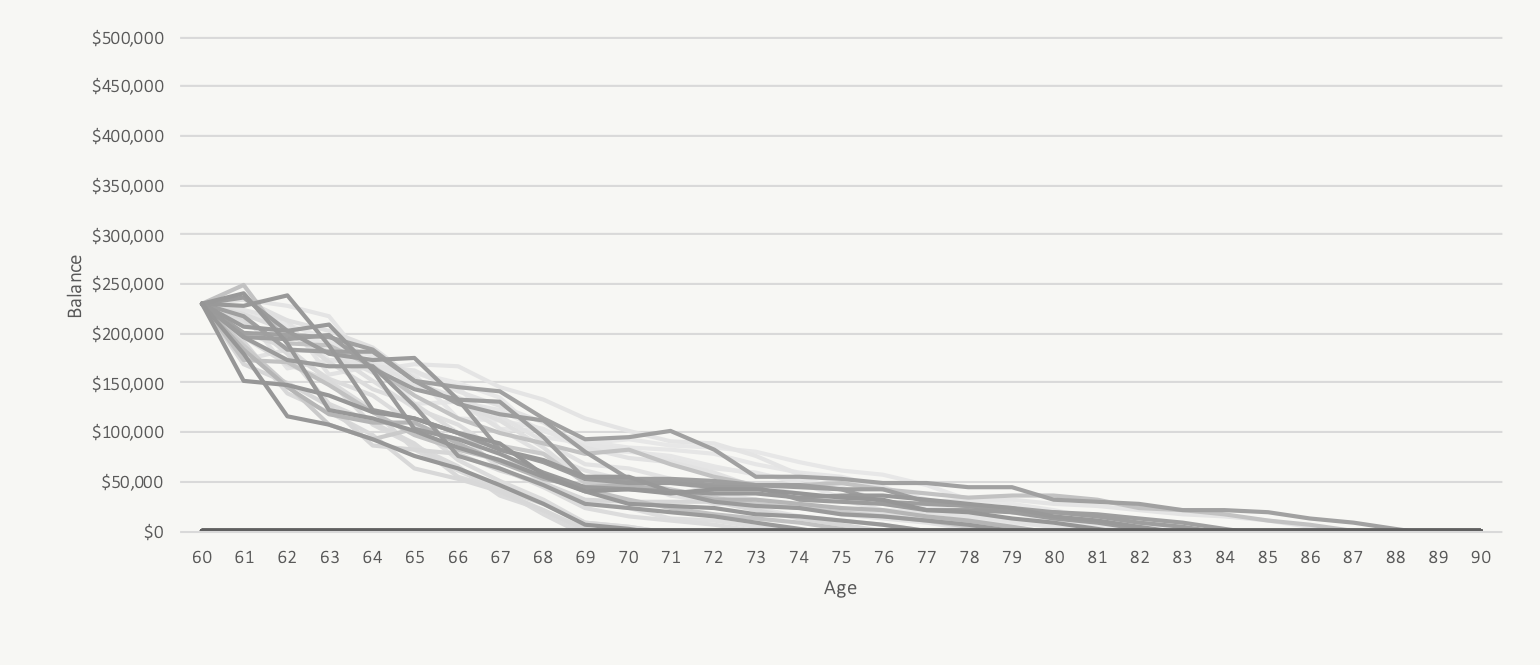
Starting CPP earlier, when faced with a series of poor investment returns, will reduce the draw on investment assets and decrease the risk of running out of money in these historical periods. As we can see below, when we focus on these “worst case” historical periods, delaying CPP to age 70 ends up being a worse decision for a retiree. In these “worst case” scenarios we would prefer to start CPP earlier than age 70 to help decrease the draw on investment assets while their value is depressed.
Worst Case: Taking CPP At Age 60
$250,000 Investment Assets And $6,400/yr in CPP
Worst Case: Taking CPP At Age 70
$250,000 Investment Assets And $14,200/yr in CPP
Strategy #3: Start CPP Retroactively To Get 12-Months Of Payments All At Once
One additional advantage for retirees who are over the age of 65 is that CPP payments can be paid retroactively for up to 12-months. The only caveat is that backdated payments cannot be earlier than age 65. Therefor this strategy only applies to those age 65 and older.
As we saw in strategy #2, there are certain investment periods where starting CPP earlier is beneficial. This is especially useful during prolonged periods of low or negative investment returns. But what if there is a correction and a quick recovery? In this case we would prefer to continue to delay CPP.
By waiting for 12-months after investment returns have gone negative we can wait and see if investment values recover, if they do recover we can continue to delay CPP, but if they do not recover we can start CPP and get 12-months of CPP paid retroactively.
What is the benefit of retroactive CPP payments? It helps reduce the draw on investment assets in the case of a prolonged decrease in investment values.
For example, if a retiree turns 65 and is faced with a large recession they can continue to delay CPP to age 66 waiting for a recovery. If no recovery happens then rather than make a large investment withdrawal at age 66 to support retirement income for the year they can instead choose to get 12-months of retroactive CPP payments and make a much smaller investment withdrawal. For a couple receiving the maximum CPP, 12-months of retroactive payments can be $28,000 or more, this significantly reduces the need to sell investment assets during a downturn.
Strategy #4: Stop CPP Within 6-Months Of Starting If Investment Values Recover Quickly
The above strategy is great for those over age 65 but isn’t available for those under age 65. Thankfully there is a similar but slightly different option available for those under age 65. The end result is similar, but it works slightly differently.
In general, CPP payments cannot be stopped once started. But there is a grace period of 6-months after CPP has started where a retiree can stop their CPP payments and pay back any payments received.
If faced with some very negative investment returns, a retiree who is under age 65 could start CPP immediately and then if they experience a quick recovery within 6-months they can stop CPP and restart it at a later date. If investment values remain strong then they can continue to delay CPP all the way until age 70.
This provides retirees below the age of 65 some flexibility with their retirement income.
Warning: There is a risk that if the paper work is late, or another error occurs, that CPP cannot be stopped, so use this strategy after appropriate thought and consideration.
Strategically Using CPP To Reduce Risk In Retirement
As we can see, the Canada Pension Plan is a huge asset in retirement and can be used strategically to help reduce investment risk and inflation rate risk.
A typical retiree should not default to taking CPP as soon as possible but should be more strategic with their CPP start date. By being strategic with CPP a retiree can reduce risk in retirement and receive a larger inflation adjusted pension for the rest of their lives.
The way CPP works means that it can be a great tool to help absorb inflation rate risk and investment risk in retirement. Many people choose to ignore these benefits (or aren’t aware of them in the first place) and simply start CPP as soon as possible. Don’t be one of these retirees. Be strategic about when you start CPP in retirement.
Join over 250,000 people reading PlanEasy.ca each year. New blog posts weekly!
Tax planning, benefit optimization, budgeting, family planning, retirement planning and more...
Join over 250,000 people reading PlanEasy.ca each year. New blog posts weekly!
Tax planning, benefit optimization, budgeting, family planning, retirement planning and more...






Thank you for raising and explaining these excellent and very rarely mentioned CPP options.
The starting CPP early and stopping within six months option is a really interesting topic for our current situation and the markets as they are today.
Thanks Bob! Yes, some of these strategic options could be a good fit during a short or prolonged downturn. It’s important to understand the timing considerations with some of these decisions because the window to stop CPP after it has started is very small. But in situations where there is a sizable stock market correction, the option to start CPP strategically is a very interesting one to consider. Thanks for the comment!